In Azure DevOps you can use Kubernetes resources to target Kubernetes clusters in an environment for deployment. You can configure your local Kubernetes cluster using Docker-desktop and then create an environment in Azure DevOps. You can use deployment job in pipeline to deploy your microservice in Kubernetes resource created in environment.
Steps:
Note: It requires a self hosted build agent to be running on this laptop where Docker-desktop kubernetes setup is running.
1. Install Docker-desktop and enable kubernetes. This will create local kubernetes setup on your laptop/desktop.
2. Now create service account, role and rolebinding to allow Azure DevOps to access this local Kubernetes cluster in Docker-desktop. The existing ServiceAccount can be mapped to a Kubernetes resource within your environment to a namespace.
–> Create Namespace
apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: dev-cluster
–> Create Service-Account
apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: dev-cluster-svc namespace: dev-cluster
–> Create Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: Role metadata: namespace: dev-cluster name: role-dev-cluster rules: - apiGroups: ["extensions", "apps",""] resources: ["*"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]
–> Create Role-binding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: RoleBinding metadata: name: role-binding-dev-cluster namespace: dev-cluster roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: Role name: role-dev-cluster subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: dev-cluster-svc namespace: dev-cluster
Note: You can change scope of Role and name of service and namespace.
3. Now create Kubernetes Resource under Environments in Azure DevOps. Login to Azure DevOps and select Environments under Pipelines as shown-
>>> On the new screen enter Name, description and select Kubernetes as shown-
>> To fill the values on new screen, use the following commands to get the values of cluster, namespace, api server url and serviceaccount’s secret value.
#get cluster names kubectl config get-contexts #get api server url kubectl config view --minify -o jsonpath='{.clusters[0].cluster.server}{"\n"}' #get service account secret names kubectl get serviceAccounts dev-cluster-svc -n dev-cluster -o=jsonpath='{.secrets[*].name}{"\n"}' #get secret value in json format kubectl get secret dev-cluster-svc-token-7scpf -n dev-cluster -o json
>> Click on “Validate and create”. It will throw error windows as shown. The reason is Azure DevOps not able to reach your local Kubernetes Server Api URL. you can click on “continue anyway”. It will create Environment.
NOTE: The only limitation is that Azure DevOps will not be able to connect to K8s resources to show the service, pods etc in the Environment screen. Also the deployment will work only with self host build agent running on this laptop where docker-desktop kubernetes cluster is setup.
>>> It will show the environment created as shown-
4. Now we will add deployment task in build pipeline-
For my sample project which is in Golang, the pipeline is
trigger:
- main
pool:
name: Self-Hosted-Agent
variables:
- group: dev
stages:
- stage: Build
jobs:
- job:
displayName: Build the application
steps:
- task: Go@0
displayName: "Go Get"
inputs:
command: 'get'
arguments: '-d'
workingDirectory: '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)'
- task: Go@0
displayName: "Go Build"
inputs:
command: 'build'
workingDirectory: '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)'
- task: qetza.replacetokens.replacetokens-task.replacetokens@3
displayName: 'Replace image version in deployment.yaml'
inputs:
rootDirectory: '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)'
targetFiles: 'deployment.yaml'
tokenPrefix: '#{'
tokenSuffix: '}#'
- task: CopyFiles@2
inputs:
SourceFolder: '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)'
Contents: 'deployment.yaml'
TargetFolder: '$(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)'
- task: PublishBuildArtifacts@1
inputs:
artifactName: drop
- task: Docker@2
displayName: Build an image
inputs:
command: build
dockerfile: '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)/Dockerfile'
buildContext: '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)'
repository: $(AWS_ECR_MAGE_URI)
- task: ECRPushImage@1
inputs:
awsCredentials: 'AWS_Service'
regionName: $(AWS_REGION)
imageSource: 'imagename'
sourceImageName: $(AWS_ECR_MAGE_URI)
sourceImageTag: $(Build.BuildId)
pushTag: $(Build.BuildId)
repositoryName: $(AWS_ECR_REPOSITORY_NAME)
- stage: Dev
dependsOn: Build
jobs:
- deployment:
displayName: Dev deploy
environment: dev
strategy:
runOnce:
deploy:
steps:
- script: kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
displayName: 'Dev Deploy'
Deployment.yaml is
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: helloworld-deploy
namespace: dev-cluster
labels:
app: hello-world-deploy
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello-world-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello-world-app
spec:
containers:
- name: helloworldapp
image: 706949302588.dkr.ecr.ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com/test-hello-world:#{Build.BuildId}#
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
resources:
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 512Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 512Mi
securityContext:
runAsUser: 1000
imagePullSecrets:
- name: aws-registry
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: hello-world-svc
name: hello-world-svc
namespace: dev-cluster
spec:
ports:
- name: helloworld
nodePort: 30423
port: 8080
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8080
selector:
app: hello-world-app
sessionAffinity: None
type: NodePort
When you run the pipeline, no need to provide Kubernetes connection details. Only Environment name needs to be set in Dev stage. It deploys the pods and service into the cluster based on resource set for Dev environment.
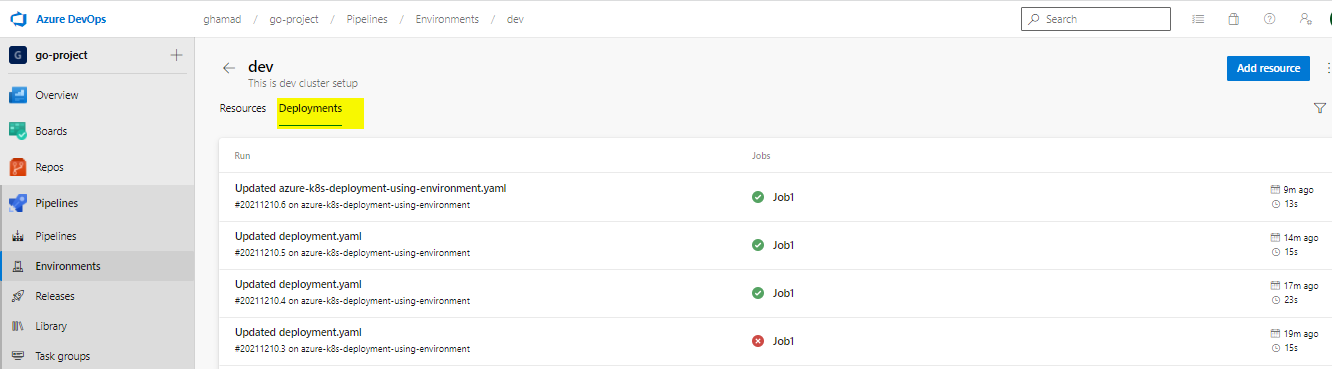
The deployment will look like below screen after successful deployment-
Also under Environments you can see the deployments
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/process/environments-kubernetes?view=azure-devops